MQTT-SN Device Plugin
Important
The MQTT-SN Interface has been replaced with the new Simple Streaming format. We still support the MQTT-SN interface, but we will not be maintaining or adding any new features going forward. Find more information on the Simple Streaming Interface in the Simple Streaming Interface Documentation
This tutorial is a continuation of the Adding Custom Device Firmware documentation
Enabling MQTT-SN Device Plugin Import
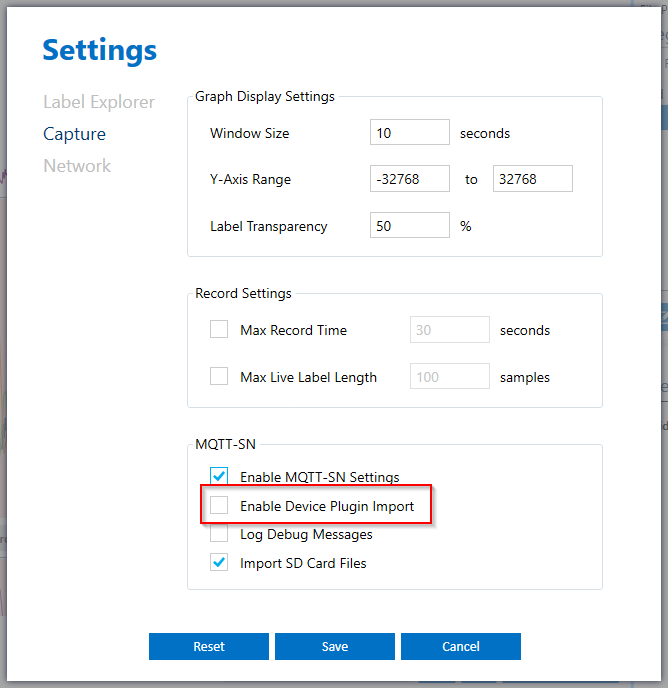
MQTT-SN Device Plugins can be imported by enabling the import setting in the Data Studio
In the Data Studio, open the menu option Edit → Settings
Open the Capture Settings
Check Enable MQTT-SN Settings
Check Enable Device Plugin Import
Download Example SSF File
The Data Studio allows you to import Device Plugins via .SSF files. Let’s go over the SSF file format and how this file will be used in the Data Studio. The SSF file format is a JSON based format with JSON properties that the Data Studio will use when configuring your Device Plugin.
Open the
Example SSF Filein any text editor and look at the properties. We will define these properties in the next section.
JSON Object Definitions
Device Plugin
uuid |
(GUID) A unique ID to identify a plugin |
device_name |
(String) Name of your device |
device_manufacturer |
(String) Name of the developer or company that manufacturers the device |
plugin_developer |
(String) Name of the developer or company that developed the Device Plugin |
firmware_download_links |
(List<Object>) A list of links that a user can use to find information on updating the device firmware for data collection. See how to define a firmware_download_link in the Plugin Link section |
documentation_links |
(List<Object>) A list of links that a user can use to find information on general tutorials or useful documentation about the device. See how to define a documentation_link in the Plugin Link section |
capture_sources |
(List<Object>) Defines each of the sensors in your device. See how to define the capture_source JSON property in the Capture Source section |
collection_methods |
(List<Object>) Defines the collection methods your board supports. See how to define the collection_method JSON property in the Collection Method section |
device_connections |
(List<Object>) Defines the connection protocols your board supports. See how to how to define the device_connection JSON property in the Device Connection section |
is_little_endian |
(Boolean) Defines if your embedded device is little endian (true) or big endian (false) |
Example Device Plugin:
{
"uuid": "00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000",
"device_name": "Your Device Name",
"device_manufacturer": "You Device Manufacturer",
"plugin_developer": "Your Device Plugin Developer",
"firmware_download_links": [
],
"documentation_links": [
],
"capture_sources": [
],
"collection_methods": [
],
"device_connections": [
],
"is_little_endian": true
}
Plugin Link
title |
(String) A user-friendly title for the link. Example: Data Collection Tutorial |
description |
(String) An optional field used to describe the contents of the link |
link |
(String) Hyperlink URL location. Example: https://sensiml.com/documentation/data-studio/flashing-data-collection-firmware.html |
Example Plugin Link:
{
"title": "Data Collection Firmware",
"description": "",
"link": "https://sensiml.com/documentation/data-studio/flashing-data-collection-firmware.html"
}
Capture Source
name |
(String) Display name for your source. Example: Motion is used to describe a source that can supply both an Accelerometer and a Gyroscope sensor. Audio is used to describe a source that is a Microphone sensor. |
part |
(String) Name of the device hardware part. Set to “Default” if a device only has one |
sample_rates |
(List<Integer>) A list of all available sample rates your device can support |
sensors |
(List<Object>) Defines the sensors your board supports. See how to how to define the sensor JSON property in the Sensor section |
sensor_combinations |
(List<Object>) MQTT-SN Only. Defines a list of definitions for making a virtual/combined sensor. This property is only used in Device Plugins that use the MQTT-SN capture protocol. This is especially useful in the case of 6-axis and 9-axis motion sensors where the data coming from all axes may wish to be treated as a single sample. See how to how to define the sensor_combination JSON property in the Sensor Combination section |
Example Capture Source:
{
"name": "Motion",
"part": "Default",
"sample_rates": [
400,
200,
100,
50
],
"sensors": [
]
}
Sensor
type |
(String) Class/name of the sensor. Example: Accelerometer |
is_default |
(Boolean) Defines if this sensor is selected as a default option in the Data Studio user interface |
column_count |
(Integer) Defines how many columns of data this sensor sends |
column_suffixes |
(List<String>) A list of strings used to describe sensors axes or channels. During data collection the Data Studio will append the column_suffix to the sensor name to create the sensor column names. For example: X | Y | Z on Accelerometer would save as AccelerometerX | AccelerometerY | AccelerometerZ |
parameters |
(List<Object>) Defines a list of sensor specific parameters such as Accelerometer range or Microphone gain. See how to how to define the sensor_parameter JSON property in the Sensor Parameter section |
can_live_stream |
(Boolean) MQTT-SN Only. Defines if this sensor can also be live-streamed while recording (using down-sampling for high data rate). This property is only used in Device Plugins that use the MQTT-SN capture protocol. |
sensor_id |
(Integer) MQTT-SN Only. Identification number of the sensor. This property is only used in Device Plugins that use the MQTT-SN capture protocol. This will be sent as an unsigned integer value to the device. It must match the definition used on your device. This is used for both data collection and for a Knowledge Pack to configure your sensors |
Example Sensor:
{
"type": "Accelerometer",
"is_default": true,
"column_count": 3,
"column_suffixes": [
"X",
"Y",
"Z"
],
}
Sensor Parameter
Sensor Parameters are used to define properties you wish to send to the sensor during data collection or recognition. For example setting the Range in an Accelerometer sensor.
name |
(String) Name of the parameter sent as an unsigned integer value to the device. It must match the definition used on your device. This is used for both data collection and for a Knowledge Pack to configure your sensors. |
values |
(List<Object>) Defines a list of available parameter values for the user to select. See how to how to define the value JSON property in the Sensor Parameter Value section |
Sensor Parameter Value
display_value |
(String) Value to be displayed to the user |
actual_value |
(Integer) Value to be used when configuring the device (saved as an unsigned 64-bit value). This can be turned into a byte array with the num_bytes property |
num_bytes |
(Integer) The number of bytes that the actual_value property needs to be converted. This is typically one byte. In the MQTT-SN Interface num_bytes is used to create the configuration array in TOPIC_SENSOR_ADD |
Sensor Paramater/Parameter Value Example:
{
"name": "Accelerometer Range",
"values": [
{
"actual_value": 20,
"num_bytes": 1,
"display_value": "+/- 2G"
},
{
"actual_value": 40,
"num_bytes": 1,
"display_value": "+/- 4G"
},
{
"actual_value": 80,
"num_bytes": 1,
"display_value": "+/- 8G"
},
{
"actual_value": 160,
"num_bytes": 1,
"display_value": "+/- 16G"
}
],
}
Sensor Combination
MQTT-SN Only: The sensor combination property is only used by the MQTT-SN protocol. Sensor combinations are used to create a virtual/combined sensor to be treated as a single sample. When all sensors in a defined combination are selected in the Data Studio configuration UI, the Data Studio will automatically use the combined_id of a given combination when configuring the device.
combined_id |
(Integer) ID for the combination |
sensors_in_combo |
(List<Integer>) Defines a list of unsigned integers that match the sensor_id properties being combined |
Sensor Combination Example:
{
"combined_id": 1229804803,
"sensors_in_combo": [
1229804865,
1229804871
]
}
Collection Method
name |
(String) Internal name for the collection method. There are three available options: |
display_name |
(String) Name to be displayed to the user |
is_default |
(Boolean) Defines if this collection method is the default option in the Data Studio user interface |
storage_path |
(String) MQTT-SN Only. Location where files being saved to the device should be stored. This property is only used in Device Plugins that use the MQTT-SN capture protocol. See TOPIC_STORAGE section of the MQTT-SN Interface Specification for more information |
Collection Method Example:
{
"name": "live",
"display_name": "Live Stream Capture",
"is_default": true
}
Device Connection
Device connections define the protocol for how you will connect to your device (Bluetooth-Low Energy, Serial/Wired UART Port, or Wi-Fi).
display_name |
(String) Name to be displayed to the user |
value |
(Integer) Value to define the connection type. There are three available options: |
is_default |
(Boolean) Defines if this connection is the default option in the Data Studio user interface |
serial_port_configuration |
(Object) Defines Serial/Wired UART Port specific configuration options. See how to how to define the serial_port_configuration JSON property in the Serial Port Configuration section |
Device Connection Example:
{
"display_name": "Serial Port",
"value": 1,
"is_default": true,
"serial_port_configuration": {
}
}
Serial Port Configuration
baud_rate |
(Integer) Speed at which you communicate. Default value is 115200. Refer to Microsoft BaudRate Documentation for more details |
stop_bits |
(Integer) Number of stop bits. Default value is 1. Refer to Microsoft StopBits Documentation for more details |
parity |
(Integer) Parity scheme. Default value is 0. Refer to Microsoft Parity Documentation for more details |
handshake |
(Integer) Handshake scheme. Default value is 0. Refer to Microsoft Handshake Documentation for more details |
max_live_sample_rate |
(Integer) The maximum frequency (in Hertz) your device is able to reliably stream sensor data without dropping packets or overflows. Default value is 0. If you are using the MQTT-SN capture protocol this is used to determine the SENSOR_COUNTDOWN field reference in TOPIC_LIVE_SET_RATE_REQ |
Example Serial Configuration:
{
"serial_port_configuration": {
"baud": 921600,
"stop_bits": 1,
"parity": 0,
"handshake": 0,
"max_live_sample_rate": 400
}
}